Social Media Accessibility
OVERVIEW
Social Media accessibility is limited in many ways, but issues accessing and understanding information are present for those with disabilities. Therefore, it is imperative that we make social media content as accessible as possible. The following sections outline accessibility features in each social media platform with a focus on Images, Hyperlinks, Hashtags, and Videos.
As a general rule for all social media content, please remember to ensure that graphics and images include adequate descriptions, videos are captioned, and hyperlinks include descriptive text. Also strive to use plain language by avoiding jargon and acronyms. Additionally, limit the use of Emojis and emoticons using characters/text because they are read literally by a screen reader and therefore cause confusion.
TWITTER BEST PRACTICES
Images
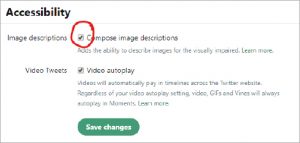
- You must turn on the Alt-Text feature in Settings.
- Navigate to Profile > Settings and Privacy > Accessibility > turn on Compose Image Descriptions. Be sure to Save the setting change.
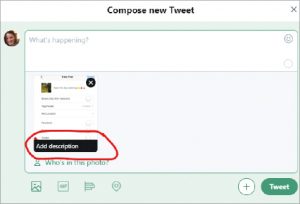
- Upload a photo to your Tweet and click “Add a Description.” A pop-up box with a description field will open. Add succinct but descriptive Alt-Text and click “Apply.”
- Return to the Compose new Tweet screen to add any additional information to your
- Tweet and click “Tweet.” This is available on Mobile and Desktop versions of Twitter.
Hyperlinks
- When tweeting a hyperlink, indicate whether you are linking to [VIDEO], [AUDIO], or [IMAGE] as seen in the example shown.
- Although Twitter has a built-in, default URL shortener, it is recommended that you use another service such as bit.ly or TinyURL that allow you to customize your link descriptions. Remember to use descriptive hyperlink text for those using screen readers.
Hashtags
- Put mentions and hashtags at the end of your tweets.
- Use camelback hashtags where the first letter of each word in the hashtag is capitalized. A camelback hashtag capitalizes the first letter of each word in a hashtag. Note the difference between #screenreaderdemo and #ScreenReaderDemo).
Video
- Make sure any linked or added video is captioned.
- PREFERRED: Upload to YouTube first and add captions if the video is not already captioned. If you need assistance with YouTube captions, please contact accessibility@olemiss.edu or refer to YouTube’s instructions for generating captions and YouTube’s instructions for editing captions.
FACEBOOK BEST PRACTICES
Images
- Facebook has an automatic alt-text generator for images that are uploaded to Facebook, however it is best practice to override the automatic text with accurate and more helpful descriptions. *Please note: Alt Text can only be edited on a computer.
- To edit the alt text when uploading a photo before you post it:
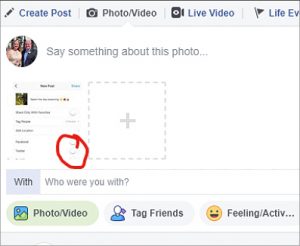
- Click Photo/Video at the top of your News Feed.
- Select the photo you want to add.
- Click Edit or the edit pencil icon in the lower-right corner of the photo thumbnail.
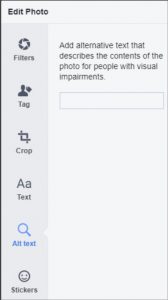
- In the new window that opens, click Alt Text in the menu at left. If there is automatically-generated text it will appear in this area.
- Enter the Alt Text for the image in the box and click “Save” in the bottom right.
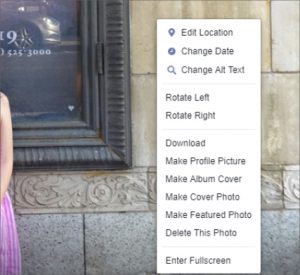
- To change the alt text of a photo after it has been posted:
- Click the photo to open it.
- Click “Options” in the bottom right and select “Change Alt Text” from the pop-up menu (hover over the photo to view the Options clickable text).
- Click “Override generated alt text” and change the alt text in the text box and click “Save.”
- Add Descriptions for each of your photos that explain the image and the context.
Hyperlinks
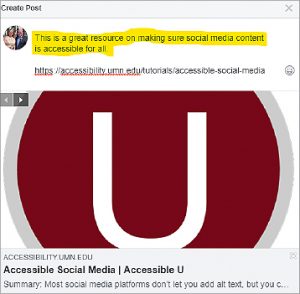
- Facebook does not have a way to customize hyperlinks, but it automatically adds a preview to the linked website that should already be accessible. If desired, you can add descriptive text about the linked site in your post copy with the copied hyperlink as shown above.
Hashtags and Tagging
- Use camelback hashtags and tag people in context when appropriate.
- When tagging someone in a photo, include that tagging information in your alt-text description. For example, “John Smith’s photo of Betty Jones taken in front of the Eiffel Tower in Paris.”
Video
- All linked or added video must be captioned.
- PREFERRED: Upload to YouTube first and add captions if the video is not already captioned. If you need assistance with YouTube captions, please contact accessibility@olemiss.edu or refer to YouTube’s instructions for generating captions and YouTube’s instructions for editing captions.
- Facebook for Business pages have a “Generate Captions” function for videos. Once a video is uploaded, the “Generate Captions” button is found by accessing the settings on the individual video.
- Please note that the auto-generated captions will not be accurate and must be edited. For information on generating and editing captions for Facebook for Business pages, visit Facebook’s help article on captioning.
INSTAGRAM BEST PRACTICES
Images
- Instagram has auto-generated alt-text image descriptions that should be edited for clarity and accuracy.
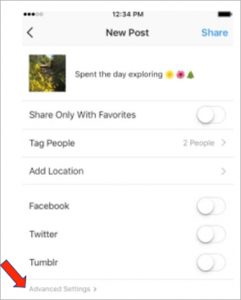
- To edit alt-text descriptions before you post:
- Tap the plus sign to and choose a photo to add to your post.
- Click Next in the upper-right corner to choose a Filter and click “Next.”
-
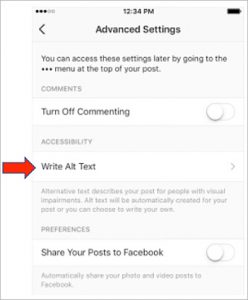
- On the Share screen, tap “Advanced Settings” found in small, gray font at the bottom of the screen.
- Tap “Write Alt Text” to describe your photo in the dialog box on the next screen and tap “Done.”
-
- Navigate back to the Share screen and write a descriptive caption and tap “Share” to post.
Videos
- Best practice is that all video uploaded to Instagram should be captioned.
- If your video is not captioned, include a transcript of the video in your caption after your post’s copy. Include the hashtag #accessibility at the end of your video transcript caption.
- For videos in Instagram Stories under 15 seconds in length, use the in-app text editor to add descriptive text about the video that can adequately serve as captions.
- Apps such as Clipomatic (PAID) create captions for use with short videos in Instagram and Instagram Stories. The captions can be edited in the app.
Hashtags and Tagging
- Use camelback hashtags and tag people in context when appropriate.
- When tagging someone in a photo, include that tagging information in your alt-text description. For example, “John Smith’s photo of Betty Jones taken in front of the Eiffel Tower in Paris.”